Magnetic Resonance Imaging
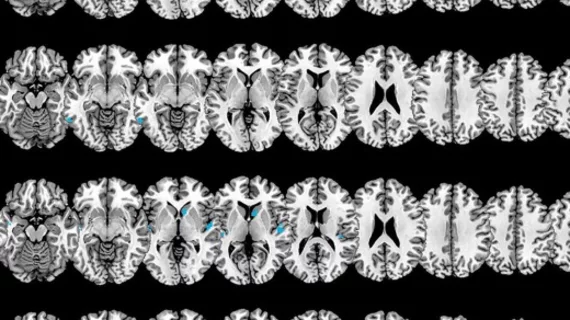
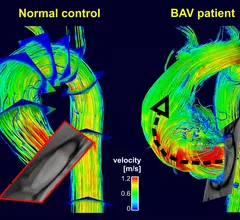
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard imaging modality for soft tissues. It produces detail cross-sectional images of soft tissue and bone anatomy, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, brain and organs, without the use of ionizing radiation. In addition to orthopedic imaging, MRI is also used for heart, brain and breast. MRI uses gadolinium contrast in many exams to highlight tissues and blood vessels, which enhances images and offers better diagnostic quality. It can also be used in conjunction with PET scans. How does MRI work? MR creates images by using powerful magnets to polarize hydrogen atoms in water (the body is made of of more than 80% water) so they face in one direction. A radiofrequency pulse is then used to ping these atoms, causing them to wobble, or resonate. The MRI coils detect this and computers can assemble images from the signals. Basic MRI scans will focus on the resonance of fat and water in two different sequences, which highlight and contrast different features in the anatomy.